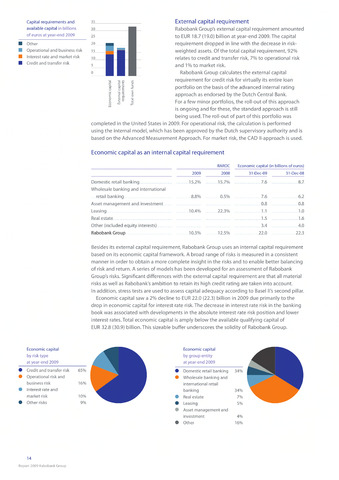
Capital requirements and
available capital in billions
of euros at year-end 2009
Other
Operational and business risk
Interest rate and market risk
Credit and transfer risk
35External capital requirement
Rabobank Group's external capital requirement amounted
to EUR 18.7 (19.0) billion at year-end 2009. The capital
requirement dropped in line with the decrease in risk-
weighted assets. Of the total capital requirement, 92%
relates to credit and transfer risk, 7% to operational risk
and 1% to market risk.
Rabobank Group calculates the external capital
requirement for credit risk for virtually its entire loan
portfolio on the basis of the advanced internal rating
approach as endorsed by the Dutch Central Bank.
For a few minor portfolios, the roll-out of this approach
is ongoing and for these, the standard approach is still
being used. The roll-out of part of this portfolio was
completed in the United States in 2009. For operational risk, the calculation is performed
using the internal model, which has been approved by the Dutch supervisory authority and is
based on the Advanced Measurement Approach. For market risk, the CAD ll-approach is used.
.ti C
Q_ U
5
C 3
aj S"
Economic capital as an internal capital requirement
Domestic.retail banking
Wholesale banking and international
retail banking
Asset management and investment
Leasing
Real.estate.
Other.(included, equity.interests)
Rabobank Group
2009
2008
15.2% 15.7%
0.5%
10.4%
10.3% 12.5%
RAROC Economic capital (in billions of euros)
31-Dec-09 31-Dec-08
7.6 8.7
7.6 6.2
0.8 0.8.
1.11.0
1.5. 1.6
3.4 4.0.
22.0 22.3.
.22.3%
Besides its external capital requirement, Rabobank Group uses an internal capital requirement
based on its economic capital framework. A broad range of risks is measured in a consistent
manner in order to obtain a more complete insight in the risks and to enable better balancing
of risk and return. A series of models has been developed for an assessment of Rabobank
Group's risks. Significant differences with the external capital requirement are that all material
risks as well as Rabobank's ambition to retain its high credit rating are taken into account.
In addition, stress tests are used to assess capital adequacy according to Basel ll's second pillar.
Economic capital saw a 2% decline to EUR 22.0 (22.3) billion in 2009 due primarily to the
drop in economic capital for interest rate risk. The decrease in interest rate risk in the banking
book was associated with developments in the absolute interest rate risk position and lower
interest rates.Total economic capital is amply below the available qualifying capital of
EUR 32.8 (30.9) billion.This sizeable buffer underscores the solidity of Rabobank Group.
Economic capital
by risk type
at year-end 2009
65%
16%
Credit and transfer risk
Operational risk and
business risk
Interest rate and
market risk 10%
Other risks 9%
Economic capital
by group entity
at year-end 2009
Domestic retail banking
34%
Wholesale banking and
international retail
banking
34%
Real estate
7%
Leasing
5%
Asset management and
investment
4%
Other
16%
14
Report 2009 Rabobank Group