Inhoudsopgave Voorwoord Bestuursverslag
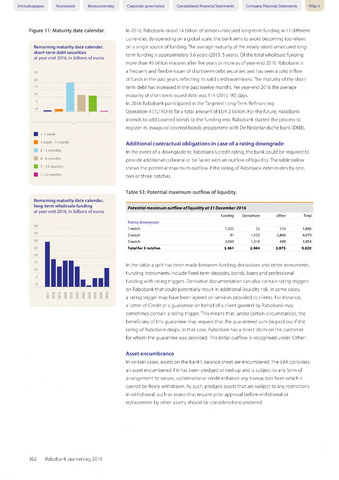
Figure 11Maturity date calendar.
Remaining maturity date calendar,
short-term debt securities
at year-end 2016, in billions of euros
25
20
Mife
1 week
1 week -1 month
2-3 months
4-6 months
7-12 months
12 months
Remaining maturity date calendar,
long-term wholesale funding
at year-end 2016, in billions of euros
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
IllllUl
NcowO'-iNm^inioio
<NrNfMrMrMfN<N<N
OOOOOOOOOOO
Corporate governance Consolidated Financial Statements Company Financial Statements Pillar 3
In 2016, Rabobank raised 14 billion of senior unsecured long-term funding in 11 different
currencies. By operating on a global scale, the bank aims to avoid becoming too reliant
on a single source of funding. The average maturity ofthe newly raised unsecured long-
term funding is approximately 5.6 years (2015: 5 years). Ofthe total wholesale funding
more than 45 billion matures after five years or more as of year-end 2016. Rabobank is
a frequent and flexible issuer of short-term debt securities and has seen a solid inflow
of funds in the past years, reflecting its solid creditworthiness. The maturity ofthe short-
term debt has increased in the past twelve months. Per year-end 2016 the average
maturity of short-term issued debt was 114 (2015: 90) days.
In 2016 Rabobank participated in theTargeted Long-Term Refinancing
Operation-ll (TLTRO-II) for a total amount of EUR 2 billion. For the future, Rabobank
intends to add covered bonds to the funding mix. Rabobank started the process to
register its inaugural covered bonds programme with De Nederlandsche bank (DNB).
Additional contractual obligations in case of a rating downgrade
In the event of a downgrade to Rabobank's credit rating, the bank could be required to
provide additional collateral or be faced with an outflow of liquidity. The table below
shows the potential maximum outflow if the rating of Rabobank deteriorates by one,
two or three notches.
Table 53: Potential maximum outflow of liquidity.
Potential maximum outflow of liquidity at 31 December 2016
Funding Derivatives
Other
Total
Rating downgrade:
1 notch
1,325 52
510
1,886
2 notch
91 1,122
2,866
4,079
3 notch
2,045 1,310
499
3,854
Total for 3 notches
3,461 2,484
3,875
9,820
In the table a split has been made between funding, derivatives and other instruments.
Funding instruments include fixed-term deposits, bonds, loans and professional
funding with rating triggers. Derivative documentation can also contain rating triggers
on Rabobank that could potentially result in additional liquidity risk. In some cases,
a rating trigger may have been agreed on services provided to clients. For instance,
a Letter of Credit or a guarantee on behalf of a client granted by Rabobank may
sometimes contain a rating trigger.This means that, under certain circumstances, the
beneficiary of this guarantee may request that the guaranteed sum be paid out if the
rating of Rabobank drops. In that case, Rabobank has a direct claim on the customer
for whom the guarantee was provided.This initial outflow is recognised under 'Other'.
Asset encumbrance
In certain cases, assets on the bank's balance sheet are encumbered. The EBA considers
an asset encumbered if it has been pledged ortied-up and is subject to any form of
arrangement to secure, collateralise or credit enhance any transaction from which it
cannot be freely withdrawn. As such, pledged assets that are subject to any restrictions
in withdrawal, such as assets that require prior approval before withdrawal or
replacement by other assets, should be considered encumbered.
362 Rabobank Jaarverslag 2016